परिचय
In दुनिया इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स का, कम-पास फिल्टर (LPFs) play a crucial role in allowing केवल कम-आवृत्ति संकेत उच्च आवृत्तियों को क्षीण करते हुए गुजरना। रोल-ऑफ of an LPF refers to the rate at which the filter attenuates संकेत इसके परे cutoff आवृत्ति. एक तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ इंगित करता है a steeper decline in सिग्नल आयाम, resulting in better filtering performance. However, achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ often requires more जटिल सर्किटरी. This is because the design of a filter with a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ involves additional components and intricate circuit configurations to effectively suppress higher frequencies. Let’s explore why a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ in an LPF necessitates more जटिल सर्किटरी.
चाबी छीन लेना
| Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Sharper roll-off | Indicates a steeper decline in signal amplitude beyond the cutoff frequency |
| अधिक जटिल सर्किट्री | Required to achieve a sharper roll-off in an LPF |
| अतिरिक्त घटक | Needed for effective suppression of higher frequencies |
| Intricate circuit configurations | Utilized to enhance the filtering performance of the LPF |
लो पास फिल्टर (एलपीएफ) को समझना

Basic Concept of LPF
लो पास फिल्टर (एलपीएफ) हैं विद्युत सर्किट that allow low-frequency signals to pass through while attenuating or blocking high-frequency signals. They are widely used in विभिन्न अनुप्रयोगों, including audio systems, communication systems, and इमेज प्रोसेसिंग.
मूल अवधारणा एलपीएफ को फ़िल्टर करना है अवांछित उच्च-आवृत्ति घटक से एक सिग्नलअनुमति दे रहा है केवल कम आवृत्ति वाले घटक to pass through. This is achieved by using निष्क्रिय या सक्रिय घटक जैसे कि प्रतिरोधक, कैपेसिटर और इंडक्टर्स।
Filter Design Considerations
When designing an LPF, कई कारण need to be considered to achieve the desired filter characteristics and performance. ये विचार शामिल हैं:
Filter Design Requirements: RSI विशिष्ठ जरूरतें of the application, such as the cutoff आवृत्ति, पासबैंड तरंग, stopband attenuation, and transition bandwidth, निर्धारित करें डिज़ाइन पैरामीटर एलपीएफ का.
फ़िल्टर प्रतिक्रिया: फ़िल्टर प्रतिक्रिया refers to how the filter behaves in terms of आयाम और चरण प्रतिक्रिया. सामान्य प्रकार of LPF responses include Butterworth, Chebyshev, and Bessel. Each response है इसका अपना समझौता है in terms of sharpness of roll-off, पासबैंड तरंग, and stopband attenuation.
फ़िल्टर विशेषता: The characteristics of an LPF, such as इसका क्रम, determine its performance. Higher-order filters provide तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ but may introduce more circuit complexity.
Filter Design Trade-offs: Designing an LPF involves trade-offs between various parameters. For example, increasing the order of the filter improves the roll-off but also increases circuit complexity and introduces more components.
Filter Design Challenges: Designing LPFs के कारण चुनौतीपूर्ण हो सकता है विचार विमर्श के बीच विभिन्न घटकों और मिलने की जरूरत है विशिष्ठ जरूरतें. उसकी आवश्यकता हैं एक गहरी समझ of सर्किट सिद्धांत और फ़िल्टर करें डिजाइन तकनीक.
Role and Application of LPF
एलपीएफ इसमें महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं विभिन्न अनुप्रयोगों जहां निष्कासन उच्च आवृत्ति शोर का या अवांछित संकेत आवश्यक है। कुछ सामान्य अनुप्रयोग of LPFs include:
ऑडियो सिस्टम: LPFs are used in audio systems to remove high-frequency noise and prevent distortion. They ensure that only the audible frequencies पुनरुत्पादित किया जाता है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप clearer and more accurate sound reproduction.
संचार प्रणाली: LPFs are used in communication systems to filter out unwanted high-frequency noise and interference. They help improve संकेत गुणवत्ता और कमी द चांसेज of डेटा दूषण संचरण के दौरान।
इमेज प्रोसेसिंग: LPFs are used in इमेज प्रोसेसिंग applications to remove high-frequency noise and enhance छवि गुणवत्ता. They help in smoothing out छवि and reducing artifacts caused by उच्च-आवृत्ति घटक.
विद्युत आपूर्ति फ़िल्टरिंग: LPFs are used in बिजली आपूर्ति सर्किट उच्च-आवृत्ति शोर को फ़िल्टर करने के लिए और तरंग वोल्टेज. वे सुनिश्चित करते हैं एक स्थिर और स्वच्छ बिजली आपूर्ति, जो के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है उचित कार्यप्रणाली of इलेक्ट्रॉनिक उपकरणों.
अंत में, कम पास फिल्टर (एलपीएफ) हैं आवश्यक घटक in विभिन्न इलेक्ट्रॉनिक प्रणालियाँ. They allow low-frequency signals to pass through while attenuating high-frequency signals. परिरूप of LPFs involves considering various parameters and trade-offs to achieve the desired filter characteristics and performance. LPFs find applications in audio systems, communication systems, इमेज प्रोसेसिंग, तथा power supply filtering, दूसरों के बीच.
The Concept of Roll-off in LPF
Definition and Importance of Roll-off
In दुनिया of electronics and signal processing, a low-pass filter (LPF) is एक मौलिक घटक वह आज्ञा देता है केवल कम-आवृत्ति संकेत क्षीण होते हुए गुजरना उच्च-आवृत्ति संकेत. एक महत्वपूर्ण पहलू of LPF design is the रोल-ऑफ़ दर, which refers to the rate at which the filter attenuates उच्च आवृत्तियाँ इसके परे cutoff आवृत्ति. रोल-ऑफ rate determines how quickly the filter reduces आयाम of these higher frequencies, अंततः आकार दे रहा है फ़िल्टर की आवृत्ति प्रतिक्रिया.
A तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ is desirable in कई आवेदन जैसा कि यह अनुमति देता है बेहतर दमन of unwanted high-frequency noise or interference. रोल-ऑफ rate is typically measured in decibels per octave (dB/oct), indicating the rate at which the filter attenuates संकेत एसटी each octave increase in frequency beyond कटऑफ बिंदु. एक तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ ensures that the LPF effectively removes unwanted frequencies, resulting in एक स्वच्छ और अधिक सटीक आउटपुट सिग्नल.
रोल-ऑफ दर है एक महत्वपूर्ण पैरामीटर to consider during LPF design, as it directly impacts the filter’s performance and characteristics. एक फिल्टर साथ में एक धीमी रोल-ऑफ अनुमति दे सकते हैं some higher-frequency components to pass through, potentially affecting वांछित संकेत. पर दूसरी तरफ, a filter with a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ निश्चित करता है की केवल वांछित कम-आवृत्ति घटक are transmitted, effectively eliminating कोई अवांछित शोर या हस्तक्षेप.
Factors Influencing the Roll-off Rate
कई कारकों प्रभावित करते हैं रोल-ऑफ़ दर of an LPF, each playing भूमिका निर्धारित करने में फ़िल्टर का समग्र प्रदर्शन और विशेषताएं. कुछ प्रमुख कारक शामिल हैं:
फ़िल्टर डिज़ाइन: विशिष्ट डिज़ाइन of the LPF, whether it is एक सक्रिय या निष्क्रिय फ़िल्टर, affects the रोल-ऑफ़ दर. Active filters, which employ जटिल सर्किटरी with active components such as operational amplifiers, can achieve steeper रोल-ऑफ़ दरकी तुलना में है निष्क्रिय फिल्टर. हालांकि, सक्रिय फिल्टर अक्सर साथ आते हैं increased circuit complexity and power requirements.
फ़िल्टर क्रम: आदेश of the LPF refers to the number of poles or stages used in the filter design. Higher-order filters generally exhibit steeper रोल-ऑफ़ दरs, allowing for better attenuation of higher frequencies. However, increasing the फ़िल्टर क्रम भी परिचय देता है additional circuit complexity और आवश्यकता हो सकती है अधिक सटीक घटक मान.
आपूर्ती बंद करने की आवृत्ति: RSI cutoff आवृत्ति of the LPF, also known as -3dB आवृत्ति, निर्धारित करता है बिंदु at which the filter starts attenuating higher frequencies. रोल-ऑफ rate is typically measured beyond इसका cutoff आवृत्ति. कम कटऑफ आवृत्तियाँ अक्सर परिणाम में और धीमा रोल-ऑफ़ दरs, जबकि उच्च कटऑफ आवृत्तियाँ के लिए अनुमति तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ विशेषताओं।
घटक सहनशीलता: सहनशीलता of घटकों में इस्तेमाल किया एलपीएफ सर्किट प्रभावित कर सकता है रोल-ऑफ़ दर. Variations in component values can lead to deviations from the desired filter response, potentially impacting the roll-off characteristics. Using उच्च परिशुद्धता घटक कम करने में मदद कर सकता है ये विविधताएँ और सुनिश्चित करें संगत फ़िल्टर प्रदर्शन.
फ़िल्टर टोपोलॉजी: The specific topology or configuration of the LPF can influence the रोल-ऑफ़ दर. विभिन्न फ़िल्टर डिज़ाइन, जैसे बटरवर्थ, चेबीशेव, या बेसेल फ़िल्टर, प्रस्ताव varying roll-off characteristics. Each topology है इसका अपना सेट है of design trade-offs and challenges, allowing engineers to choose सबसे उपयुक्त विकल्प पर आधारित आवेदन आवश्यकताएँ.
सारांश में, रोल-ऑफ़ दर is एक महत्वपूर्ण पहलू of LPF design, determining how effectively the filter attenuates higher frequencies beyond its cutoff point. By considering factors such as filter design, order, cutoff आवृत्ति, घटक सहनशीलता, and topology, engineers can tailor the roll-off characteristics to meet the विशिष्ठ जरूरतें of उनके अनुप्रयोग. हासिल करने बांछित रोल-ऑफ़ दर सुनिश्चित इष्टतम फ़िल्टर प्रदर्शन और बढ़ाता है समग्र कार्यक्षमता एलपीएफ का.
The Relationship between Roll-off Sharpness and Circuit Complexity
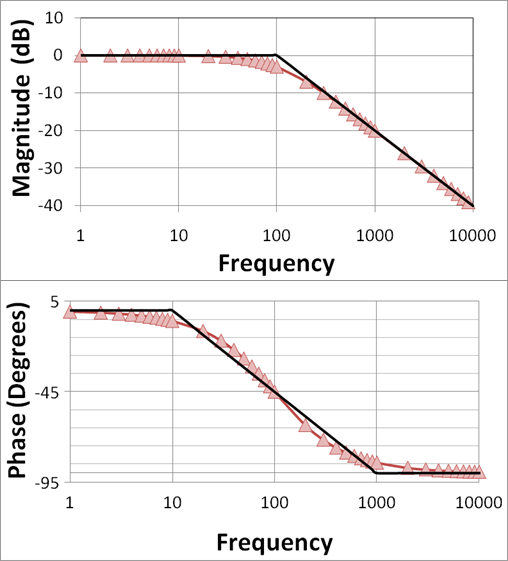
How Sharpness of Roll-off Affects Circuit Design
तीक्ष्णता of roll-off in a filter refers to how quickly the filter attenuates frequencies beyond its cutoff point. In अन्य शब्द, it determines how effectively the filter removes unwanted frequencies. रोल-ऑफ sharpness is एक महत्वपूर्ण विशेषता of a filter as it directly affects its performance and functionality.
When designing a filter, such as a low-pass filter (LPF), la roll-off sharpness plays a crucial role in determining the complexity of the circuitry required. A तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ और चाहिए जटिल सर्किटरी to achieve the desired filter response. This is because a steeper roll-off necessitates additional components and more intricate डिजाइन तकनीक to achieve the desired filter characteristics.
यह समझने के लिए कि ए तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ और चाहिए जटिल सर्किटरी, let’s consider the design of a low-pass filter. एक कम-पास फ़िल्टर allows frequencies below एक निश्चित कटऑफ बिंदु to pass through while attenuating frequencies above it. रोल-ऑफ region is where the filter transitions from allowing frequencies to attenuating them.
In a simple low-pass filter design, the roll-off is typically gradual, meaning that the filter gradually attenuates frequencies beyond कटऑफ बिंदु. इसके साथ हासिल किया जा सकता है एक बुनियादी सर्किट consisting of passive components such as resistors and capacitors. However, if a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ is desired, the circuit complexity needs to increase.
प्राप्त करने के लिए ए तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़, अधिक जटिल सर्किटरी is required. This may involve इसके अलावा of active components such as operational amplifiers (op-amps) or more advanced filter topologies. सक्रिय घटक can provide gain and feedback, allowing for greater control over the filter response. Additionally, more advanced filter topologiesइस तरह के रूप में, उच्च-क्रम फ़िल्टर, प्राप्त करने के लिए नियोजित किया जा सकता है तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ विशेषताओं।
The Need for More Complex Circuitry for Sharper Roll-off
जरूरत और अधिक के लिए जटिल सर्किटरी से उपजते हैं व्यापार बंद and challenges associated with achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ in filter design. While a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ can provide better filtering performance by attenuating unwanted frequencies more effectively, it comes with certain design considerations और आवश्यकताओं।
एक के मुख्य चुनौतियाँ in designing a filter with a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ is maintaining stability. As the roll-off becomes steeper, the filter can become more susceptible to instability, oscillations, and ringing. This requires careful consideration of component values, feedback configurations, तथा मुआवज़ा तकनीक यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए स्थिर संचालन.
एक और विचार is प्रभाव on the overall filter design. एक तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ अक्सर परिणाम होता है एक संकीर्ण संक्रमण बैंड, which means that the filter may exhibit a larger group delay और चरण विकृति. इसका असर पड़ सकता है फ़िल्टर की प्रतिक्रिया सेवा मेरे time-domain signals और परिचय दें अवांछित कलाकृतियाँ. डिजाइनरों को सावधानीपूर्वक संतुलन बनाना चाहिए बांछित roll-off sharpness साथ में अन्य प्रदर्शन पैरामीटर मिलना विशिष्ठ जरूरतें आवेदन के
संक्षेप में, रिश्ता के बीच roll-off sharpness and circuit complexity in filter design is evident. A तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ और चाहिए जटिल सर्किटरी due to the need for additional components and advanced डिजाइन तकनीक. However, achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ also presents challenges and trade-offs that designers must carefully consider. By understanding ये रिश्ते और बनाने सूचित डिज़ाइन विकल्प, engineers can create filters that meet बांछित प्रदर्शन संबंधी जरूरतें while managing circuit complexity effectively.
Detailed Explanation: Why Sharper Roll-off Requires More Complex Circuitry
The Role of Additional Components in Achieving Sharper Roll-off
When designing a low-pass filter (LPF) to achieve a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़, it is necessary to incorporate additional components into the circuitry. ये अतिरिक्त घटक play a crucial role in shaping the filter response and improving its performance.
एक के प्रमुख घटक used in achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ is संधारित्र. Capacitors are widely used in filter design due to उनकी क्षमता संग्रहित करना और जारी करना विद्युत ऊर्जा. In an LPF, capacitors are used to block high-frequency signals while allowing low-frequency signals to pass through. By strategically placing capacitors in the circuit, फ़िल्टर का रोल-ऑफ़ can be made steeper, resulting in better attenuation of unwanted high-frequency noise.
एक अन्य महत्वपूर्ण घटक used in achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ is प्रारंभ करनेवाला. Inductors are निष्क्रिय इलेक्ट्रॉनिक घटक जो ऊर्जा को संग्रहित करता है एक चुंबकीय क्षेत्र. In LPF design, inductors are used to block low-frequency signals while allowing high-frequency signals to pass through. By incorporating inductors into the circuit, फ़िल्टर का रोल-ऑफ़ can be made steeper, enhancing its ability to reject अवांछित कम-आवृत्ति हस्तक्षेप.
In addition to capacitors and inductors, resistors are also commonly used in filter design to control प्रवाह of current. By strategically selecting resistor values, फ़िल्टर की विशेषताएँ हासिल करने के लिए इसे दुरुस्त किया जा सकता है बांछित roll-off sharpness. Resistors play a crucial role in determining the cutoff आवृत्ति और समग्र प्रदर्शन फ़िल्टर का.
The Trade-off between Roll-off Sharpness and Circuit Complexity
While incorporating additional components into the circuitry allows for a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़, it also increases the complexity of समग्र सर्किट डिजाइन. As more components are added, the circuit becomes more intricate, requiring careful consideration of various design trade-offs और चुनौतियाँ.
एक के the main trade-offs in filter design is संतुलन के बीच roll-off sharpness and circuit complexity. Achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ often requires the use of more जटिल सर्किटरीशामिल है एक बड़ी संख्या घटकों का और more intricate connections. इस बढ़ी हुई जटिलता कारण बनना उच्च विनिर्माण लागत, वृद्धि हुई बिजली की खपत, तथा संभावित विश्वसनीयता मुद्दे.
Furthermore, as the circuit complexity increases, so does जोखिम परिचय कराने का अवांछित प्रभाव जैसे संकेत विकृति, चरण परिवर्तन, तथा प्रतिबाधा बेमेल. ये कारक need to be carefully considered and mitigated to ensure the filter performs as intended.
Designing filters with तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ characteristics also poses challenges in meeting विशिष्ट डिज़ाइन आवश्यकताएँ. As the roll-off becomes steeper, the filter’s performance may be more sensitive to घटक सहनशीलता, तापमान भिन्नता, तथा अन्य बाहरी कारक. This requires careful consideration during डिजाइन चरण to ensure the filter meets वांछित विशिष्टताएँ के अंतर्गत विभिन्न परिचालन स्थितियाँ.
In conclusion, achieving a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ in filter design requires निगमन of additional components such as capacitors, inductors, and resistors. While इन घटकों enhance the filter’s performance, they also increase circuit complexity and introduce design trade-offs and challenges. Engineers must carefully balance la roll-off sharpness with circuit complexity to meet the desired filter design requirements.
Practical Examples and Analysis

Case Study: Designing LPF with Sharper Roll-off
In इस मामले का अध्ययन, we will explore the design of एक लो-पास फ़िल्टर (एलपीएफ) ए के साथ तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़. एक एल.पी.एफ. is एक इलेक्ट्रॉनिक सर्किट जो उच्च-आवृत्ति संकेतों को क्षीण करते हुए कम-आवृत्ति संकेतों को गुजरने की अनुमति देता है। रोल-ऑफ refers to the rate at which the filter attenuates उच्च-आवृत्ति संकेत इसके परे cutoff आवृत्ति.
Designing a LPF with a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ के कारण चुनौतीपूर्ण हो सकता है जटिल सर्किटरी involved. However, it is necessary in applications where सटीक फ़िल्टरिंग is required to eliminate अवांछित शोर or interference. Let’s analyze चुनौतियाँ and solutions in implementing such जटिल सर्किटरी.
Analysis: Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Complex Circuitry
एक के मुख्य चुनौतियाँ in designing a LPF with a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ is the circuit complexity. As the roll-off becomes steeper, the number of components and the complexity of सर्किट में वृद्धि। यह करने के लिए नेतृत्व कर सकते हैं उच्च विनिर्माण लागत और संभावित विश्वसनीयता मुद्दे. Engineers need to carefully balance the desired filter characteristics with व्यावहारिक सीमाएँ of the circuit complexity.
एक और चुनौती is व्यापार बंद involved in filter design. A तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ अक्सर आता है खर्च of अन्य फ़िल्टर प्रदर्शन पैरामीटरइस तरह के रूप में, पासबैंड तरंग and stopband attenuation. Engineers need to consider the विशिष्ठ जरूरतें of the application and make डिजाइन निर्णय तदनुसार।
पर काबू पाने ये चुनौतियाँ, कई डिज़ाइन संबंधी विचार and solutions can be implemented. Here are कुछ उदाहरण:
Active Filter Design: Active filters, which use active components such as operational amplifiers, can provide अधिक लाभ और बेहतर नियंत्रण over the filter response. This allows for a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ while reducing the number of passive components required.
Higher Order Filters: Increasing the order of the filter can result in a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़. उच्च क्रम के फ़िल्टर है अधिक डंडे and zeros, allowing for greater control over the filter response. However, this also increases the circuit complexity and introduces additional design challenges.
Cascading Filters: By cascading कई चरण प्रत्येक फिल्टर के साथ a moderate roll-off, a sharper overall roll-off पाया जा सकता है। यह दृष्टिकोण की अनुमति देता है एक अधिक क्रमिक संक्रमण between the passband and stopband, reducing the design challenges के साथ जुड़े a single high-order filter.
अनुकूलन तकनीक: विभिन्न अनुकूलन तकनीकें, जैसे का उपयोग कंप्यूटर-सहायता प्राप्त डिज़ाइन उपकरण और सिमुलेशन सॉफ्टवेयर, can help in achieving the desired filter characteristics while minimizing the circuit complexity. ये उपकरण इंजीनियरों को विश्लेषण करने की अनुमति दें विभिन्न डिज़ाइन विकल्प और बनाओ सूचित निर्णय.
In conclusion, designing a LPF with a तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ involves overcoming challenges related to circuit complexity and trade-offs in फ़िल्टर प्रदर्शन. विचार करके विशिष्ठ जरूरतें of the application and implementing appropriate design solutions, engineers can achieve the desired filter characteristics while maintaining पैमाना between performance and complexity.
निष्कर्ष
अंत में, ए तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ in लो पास फिल्टर (एलपीएफ)) often requires more जटिल सर्किटरी की वजह से प्रकृति of फ़िल्टरिंग प्रक्रिया. एक तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ को संदर्भित करता है ढलान of the filter’s attenuation curve, indicating how quickly the filter attenuates frequencies above its cutoff point.
प्राप्त करने के लिए ए तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़, अधिक जटिल सर्किटरी is needed because it requires additional components and stages in the filter design. ये अतिरिक्त घटक and stages help to increase the filter’s selectivity and improve its ability to attenuate unwanted frequencies effectively.
थोड़ी देर तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ can provide better filtering performance, it comes at कीमत of बढ़ी हुई जटिलता और संभावित रूप से उच्च विनिर्माण लागत। इसलिए, फैसला एक का उपयोग करने के लिए तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ in an LPF should be based on the विशिष्ठ जरूरतें and constraints of the application.
Why does a sharper roll-off in an LPF often require more complex circuitry? How does it relate to the impact of signal amplitude on energy?
Signal energy and amplitude relationship explained.
The relationship between a sharper roll-off in a low-pass filter (LPF) and the complexity of the circuitry is closely tied to the impact of the signal’s amplitude on its energy. In an LPF, a steeper roll-off refers to a rapid decrease in the magnitude of frequencies beyond a specific cut-off point. Achieving a sharper roll-off often requires more intricate circuit design and components to accurately filter out high-frequency noise. The amplitude of a signal, on the other hand, relates to the magnitude or strength of the signal. As the amplitude increases, the energy of the signal also increases. Therefore, when dealing with signals of higher amplitude, it becomes crucial to implement a more complex LPF to ensure effective filtering without significantly impacting the energy of the signal.
आम सवाल-जवाब
Q1: What is a low-pass filter (LPF)?
A1: एक कम-पास फ़िल्टर (एलपीएफ) है एक प्रकार of filter that allows low-frequency signals to pass through while attenuating high-frequency signals.
Q2: What is a filter response?
A2: फ़िल्टर प्रतिक्रिया को संदर्भित करता है व्यवहार of a filter in terms of how it alters आयाम और का चरण विभिन्न आवृत्तियों in इनपुट सिग्नल.
Q3: What are the characteristics of a filter?
A3: The characteristics of a filter include इसकी आवृत्ति प्रतिक्रिया, फ़िल्टर क्रम, रोल-ऑफ़ दर, पासबैंड तरंग, stopband attenuation, and चरण प्रतिक्रिया.
Q4: What is filter performance?
A4: फ़िल्टर प्रदर्शन refers to how well a filter meets इसके डिजाइन विनिर्देश, such as its ability to attenuate unwanted frequencies and preserve वांछित आवृत्तियाँ.
Q5: What are the trade-offs in filter design?
A5: Filter design trade-offs involve balancing कई कारक जैसे फ़िल्टर जटिलता, performance, cost, बिजली की खपत, and size to achieve the desired filter characteristics.
Q6: What are the challenges in filter design?
A6: Filter design challenges include achieving the desired filter response, meeting डिजाइन विनिर्देश, minimizing circuit complexity, managing घटक सहनशीलता, और संबोधन संकेत विकृति मुद्दे।
Q7: What are the requirements for filter design?
A7: Filter design requirements include specifying वांछित पासबैंड और स्टॉपबैंड आवृत्तियाँ, पासबैंड तरंग, stopband attenuation, रोल-ऑफ़ दर, तथा चरण प्रतिक्रिया.
Q8: What are the considerations in filter design?
A8: Filter design considerations include selecting उपयुक्त फ़िल्टर टोपोलॉजी, का निर्धारण फ़िल्टर क्रम, चुनना सही घटकके प्रबंध घटक सहनशीलता, and optimizing the filter response.
Q9: What is circuit complexity in filter design?
A9: सर्किट जटिलता को संदर्भित करता है स्तर of complexity in the design and implementation of फिल्टर सर्किट्री, which can vary depending on the desired filter characteristics and प्रदर्शन संबंधी जरूरतें.
Q10: What is a sharper roll-off in filter design?
ए10: ए तेज़ रोल-ऑफ़ को संदर्भित करता है एक तीव्र क्षीणन of frequencies outside the passband of a filter, indicating a more aggressive suppression of unwanted frequencies.
यह भी पढ़ें:
- गेट लेवल लॉजिक को कैसे अनुकूलित करें
- क्या जेनर डायोड विशिष्ट अनुप्रयोगों के लिए अन्य डायोड के साथ मिलकर काम कर सकते हैं?
- सुधार के लिए डायोड कहाँ रखा जाना चाहिए?
- फ्लिप फ्लॉप में एज ट्रिगरिंग कैसे काम करती है?
- फ्लिप फ्लॉप में फीडबैक लूप क्यों आवश्यक हैं?
- संचार प्रणालियों के संदर्भ में सिग्नल क्या है?
- नॉन इनवर्टिंग ऑप एम्प वोल्टेज फॉलोअर
- एलपीएफ की कटऑफ आवृत्ति क्या है?
- एलईडी ड्राइवर का उपयोग करना कब उचित है?
- एसआर फ्लिप फ्लॉप क्या है

टेकीसाइंस कोर एसएमई टीम भौतिकी, रसायन विज्ञान, प्रौद्योगिकी, इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स और इलेक्ट्रिकल इंजीनियरिंग, ऑटोमोटिव, मैकेनिकल इंजीनियरिंग सहित विभिन्न वैज्ञानिक और तकनीकी क्षेत्रों के अनुभवी विषय विशेषज्ञों का एक समूह है। हमारी टीम TechieScience.com वेबसाइट के लिए विज्ञान और प्रौद्योगिकी विषयों की एक विस्तृत श्रृंखला पर उच्च-गुणवत्ता, अच्छी तरह से शोधित लेख बनाने के लिए सहयोग करती है।
हमारे सभी वरिष्ठ एसएमई के पास संबंधित क्षेत्रों में 7 वर्षों से अधिक का अनुभव है। वे या तो कामकाजी उद्योग पेशेवर हैं या विभिन्न विश्वविद्यालयों से जुड़े हैं। संदर्भ देना हमारे लेखक हमारे मुख्य एसएमई के बारे में जानने के लिए पेज।

नमस्कार साथी पाठक,
टेकीसाइंस में हम एक छोटी टीम हैं, जो बड़े खिलाड़ियों के बीच कड़ी मेहनत कर रही है। यदि आप जो देखते हैं वह आपको पसंद आता है, तो कृपया हमारी सामग्री को सोशल मीडिया पर साझा करें। आपके समर्थन से बहुत फर्क पड़ता है. धन्यवाद!